

大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平时空特征与影响路径研究
|
余凤龙(1978—),男,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为旅游消费与饮食文化旅游。E-mail:frankid@sina.com |
收稿日期: 2024-11-02
修回日期: 2025-04-27
网络出版日期: 2025-07-07
基金资助
江苏高校哲学社会科学研究重大项目(2022SJZD027)
中国大运河研究院重点项目(DYH202307)
国家社会科学基金艺术学项目(23BH164)
国家自然科学基金面上项目(42071193)
Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Impact Path of Culture and Tourism Consumption Level in Cities along the Jiangsu-Zhejiang Section of the Grand Canal
Received date: 2024-11-02
Revised date: 2025-04-27
Online published: 2025-07-07
推进文旅融合发展和提升人民生活品质是大运河国家文化公园建设的内在要求和重要目标,大运河沿线城市文旅消费水平的研究为其提供理论依据与实践路径。文章以中国大运河江浙段13个城市为研究区域,从文旅消费环境、文旅消费能力、文旅消费支出和文旅消费满意度4个维度构建文旅消费水平评价指标体系,运用数理统计、模糊集定性比较分析等方法,系统探究了大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平的时空特征与影响路径。研究发现:①大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平呈现波动性增长态势,其中浙江段消费水平相对较高,苏州和杭州市是文旅消费水平的2个核心,江浙段沿线城市差异逐年减缓。②大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平的4个维度具有明显时空分异性,其中时序上文旅消费能力指数逐年增长,文旅消费满意度变动幅度较小;空间上文旅消费环境指数差异最大,而文旅消费支出和文旅消费满意度地区差异相对较小。③从构建“供给—需求—政策”的文旅消费组态影响因素模型分析看,文旅消费水平受资源产品基础、服务设施水平、经济收入水平、文化教育水平和政府支持引导5个变量的组态影响,高文旅消费水平组态路径可分为环境供给驱动型、内在需求驱动型和供需多元联动型。
余凤龙 , 徐留倩 , 侯兵 . 大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平时空特征与影响路径研究[J]. 经济地理, 2025 , 45(5) : 191 -201 . DOI: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2025.05.020
Promoting the integrated development of culture and tourism and improving people's quality of life are intrinsic requirements and important goals for the construction of the Grand Canal National Cultural Park. The study of cultural and tourism consumption levels in cities along the canal provides theoretical support and practical pathways for its development. This article takes 13 cities in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang section of the Grand Canal in China as the research area, and constructs an evaluation system for culture and tourism consumption level from four dimensions: culture and tourism consumption environment, culture and tourism consumption capacity, culture and tourism consumption expenditure, and culture and tourism consumption satisfaction. By comprehensively using mathematical statistics and fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis, this article systematically explores the spatiotemporal characteristics and impact paths of culture and tourism consumption level in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang section of the Grand Canal. The results show that: 1) The culture and tourism consumption level shows a fluctuating growth trend, presenting a "dual core" spatial pattern of Suzhou and Hangzhou, with regional differences gradually decreasing year by year. 2) The four dimensions of culture and tourism consumption level have obvious differentiation. The index of culture and tourism consumption capacity increases year by year, the index of culture and tourism consumption satisfaction changes slightly. The index of culture and tourism consumption environment has the largest regional difference, while it has relatively small regional differences in terms of culture and tourism consumption expenditure and culture and tourism consumption satisfaction. 3) It constructs a configuration factor framework of culture and tourism consumption from the perspectives of supply-demand-policy, the culture and tourism consumption level is influenced by the configuration of five variables: resource product foundation, service facility level, economic income level, culture and educational level, and government support and guidance. The configuration path of high level of culture and tourism consumption can be divided into three types: environmental supply type, internal demand type, and supply-demand diversified linkage type.
表1 文旅消费水平的评价指标体系及说明Tab.1 Evaluation index system of culture and tourism consumption level and its explanation |
| 维度 | 具体要素 | 衡量指标 | 权重 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文旅消费环境 | 文旅产业经济水平 | 文化、体育和娱乐业生产总值(亿元) | 0.0816 | [30] |
| 国内旅游收入(亿元) | 0.0750 | [29] | ||
| 文旅产业从业人员 | 文化、体育和娱乐业从业人员数(万人) | 0.0866 | - | |
| 住宿和餐饮从业人数(万人) | 0.0967 | - | ||
| 旅游接待人次 | 国内旅游接待人次(万人次) | 0.0691 | [18] | |
| 第三产业比重 | 第三产业占GDP比重(%) | 0.0511 | - | |
| 政府支持力度 | 文化旅游体育与传媒支出占财政支出比重(%) | 0.0485 | [31] | |
| 文旅消费能力 | 物质消费能力 | 人均可支配收入(元/人) | 0.0677 | [32] |
| 地区生活水平 | 人均GDP(元/人) | 0.0816 | [30] | |
| 文旅消费支出 | 文教娱消费支出 | 人均文教娱乐支出(元/人) | 0.0909 | [33] |
| 文教娱消费率 | 人均文教娱乐支出占消费支出比重(%) | 0.0736 | [17] | |
| 边际文旅消费倾向 | 居民文化消费增量/可支配收入增量(%) | 0.0675 | [17] | |
| 文旅消费满意度 | 文旅消费价格指数 | 文化教育娱乐价格指数(上年=100) | 0.0536 | [29] |
| 文旅设施满足率 | 人均拥有公共图书馆藏量(册/人) | 0.0565 | [18] |
表2 大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平指数Tab.2 Culture and tourism consumption level index in cities of research area |
| 区域 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 江浙段 | 0.266 | 0.279 | 0.314 | 0.333 | 0.347 | 0.366 | 0.395 | 0.357 | 0.389 | 0.367 |
| 江苏段 | 0.247 | 0.265 | 0.289 | 0.319 | 0.333 | 0.344 | 0.369 | 0.337 | 0.387 | 0.356 |
| 浙江段 | 0.296 | 0.302 | 0.354 | 0.356 | 0.369 | 0.402 | 0.437 | 0.388 | 0.393 | 0.385 |
| 徐州 | 0.160 | 0.167 | 0.184 | 0.186 | 0.228 | 0.230 | 0.254 | 0.229 | 0.269 | 0.232 |
| 宿迁 | 0.159 | 0.157 | 0.190 | 0.194 | 0.156 | 0.187 | 0.250 | 0.218 | 0.261 | 0.245 |
| 淮安 | 0.175 | 0.179 | 0.211 | 0.239 | 0.251 | 0.243 | 0.262 | 0.228 | 0.256 | 0.243 |
| 扬州 | 0.203 | 0.248 | 0.271 | 0.280 | 0.291 | 0.320 | 0.323 | 0.323 | 0.366 | 0.335 |
| 镇江 | 0.227 | 0.268 | 0.304 | 0.344 | 0.351 | 0.355 | 0.369 | 0.306 | 0.392 | 0.329 |
| 常州 | 0.260 | 0.305 | 0.330 | 0.378 | 0.430 | 0.431 | 0.413 | 0.399 | 0.450 | 0.432 |
| 无锡 | 0.349 | 0.325 | 0.362 | 0.418 | 0.403 | 0.421 | 0.473 | 0.445 | 0.490 | 0.462 |
| 苏州 | 0.442 | 0.472 | 0.461 | 0.509 | 0.549 | 0.563 | 0.609 | 0.548 | 0.612 | 0.567 |
| 湖州 | 0.167 | 0.189 | 0.224 | 0.239 | 0.211 | 0.297 | 0.308 | 0.269 | 0.257 | 0.277 |
| 嘉兴 | 0.241 | 0.247 | 0.298 | 0.274 | 0.304 | 0.305 | 0.342 | 0.349 | 0.375 | 0.341 |
| 杭州 | 0.521 | 0.554 | 0.618 | 0.620 | 0.566 | 0.686 | 0.715 | 0.586 | 0.584 | 0.549 |
| 绍兴 | 0.238 | 0.191 | 0.278 | 0.274 | 0.347 | 0.301 | 0.334 | 0.339 | 0.331 | 0.344 |
| 宁波 | 0.312 | 0.328 | 0.354 | 0.375 | 0.418 | 0.422 | 0.484 | 0.395 | 0.421 | 0.412 |
表3 大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平的维度差异Tab.3 Differences in four dimensions of culture and tourism consumption level in cities of research area |
| 维度 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文旅消费能力 | C | 0.546 | 0.480 | 0.443 | 0.410 | 0.394 | 0.368 | 0.352 | 0.332 | 0.319 | 0.306 |
| G | 0.334 | 0.290 | 0.267 | 0.247 | 0.239 | 0.222 | 0.211 | 0.197 | 0.190 | 0.182 | |
| 文旅消费支出 | C | 0.232 | 0.316 | 0.228 | 0.215 | 0.336 | 0.232 | 0.199 | 0.344 | 0.277 | 0.272 |
| G | 0.141 | 0.191 | 0.141 | 0.129 | 0.185 | 0.142 | 0.123 | 0.206 | 0.164 | 0.166 | |
| 文旅消费环境 | C | 0.806 | 0.752 | 0.730 | 0.680 | 0.553 | 0.660 | 0.623 | 0.560 | 0.559 | 0.617 |
| G | 0.445 | 0.416 | 0.393 | 0.372 | 0.325 | 0.357 | 0.331 | 0.317 | 0.318 | 0.347 | |
| 文旅消费满意度 | C | 0.278 | 0.366 | 0.339 | 0.232 | 0.345 | 0.330 | 0.313 | 0.247 | 0.239 | 0.258 |
| G | 0.170 | 0.221 | 0.177 | 0.140 | 0.200 | 0.199 | 0.173 | 0.152 | 0.145 | 0.154 | |
表4 单变量必要条件分析Tab.4 Results of necessary condition analysis |
| 条件变量 | 高文旅消费水平 | 非高文旅消费水平 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一致性 | 覆盖率 | 一致性 | 覆盖率 | |
| 资源产品基础 | 0.832960 | 0.802404 | 0.493630 | 0.513563 |
| ~资源产品基础 | 0.495040 | 0.475123 | 0.810074 | 0.839680 |
| 服务设施水平 | 0.821440 | 0.890701 | 0.441185 | 0.516655 |
| ~服务设施水平 | 0.554240 | 0.478718 | 0.906666 | 0.845771 |
| 经济收入水平 | 0.896960 | 0.873209 | 0.457185 | 0.480685 |
| ~经济收入水平 | 0.466560 | 0.443161 | 0.879407 | 0.902128 |
| 文化教育水平 | 0.861120 | 0.824954 | 0.472889 | 0.489270 |
| ~文化教育水平 | 0.466880 | 0.450587 | 0.830815 | 0.865966 |
| 政府支持引导 | 0.578240 | 0.599933 | 0.624296 | 0.699535 |
| ~政府支持引导 | 0.710400 | 0.636468 | 0.642963 | 0.622133 |
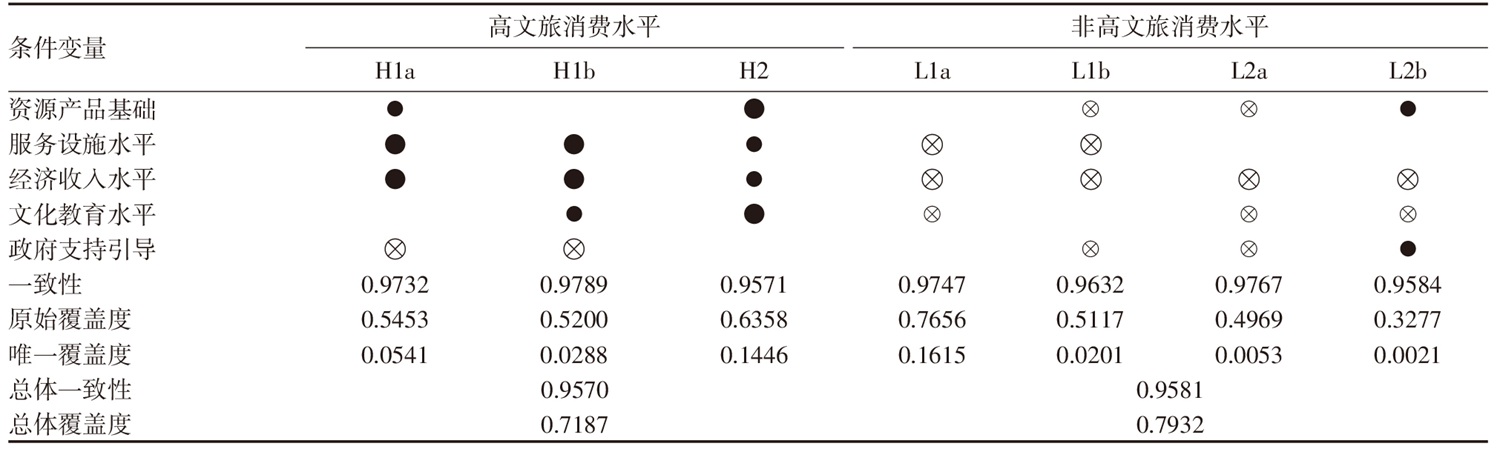
 ”(大图)代表核心条件存在,“
”(大图)代表核心条件存在,“  ”(小图)代表边缘条件存在,“
”(小图)代表边缘条件存在,“  ”(大图)代表核心条件缺失,“
”(大图)代表核心条件缺失,“  ”(小图)代表边缘条件缺失,对组态分析结果进行规范表示。由表5可知,高文旅消费水平的组态影响路径有3条,非高文旅消费水平的组态影响路径有4条。其中,高文旅消费水平和非高文旅消费水平组态路径一致性均大于0.9,大于可接受水平0.8;总体解的覆盖度分别为0.7187、0.7932,表明组态路径对高和非高文旅消费水平结果都具有较强的解释力。
”(小图)代表边缘条件缺失,对组态分析结果进行规范表示。由表5可知,高文旅消费水平的组态影响路径有3条,非高文旅消费水平的组态影响路径有4条。其中,高文旅消费水平和非高文旅消费水平组态路径一致性均大于0.9,大于可接受水平0.8;总体解的覆盖度分别为0.7187、0.7932,表明组态路径对高和非高文旅消费水平结果都具有较强的解释力。表5 大运河江浙段沿线城市文旅消费水平的组态影响路径Tab.5 Configuration influence paths of culture and tourism consumption level in cities of research area |
 |
注: |
| [1] |
王晓静. 人文城市建设视域下的文化和旅游消费[J]. 江西社会科学, 2021, 41(9):246-253.
|
| [2] |
张梦, 郭养红, 付晓蓉. 旅游消费者行为研究的过去、现在和未来——基于引证研究法的研究[J]. 旅游学刊, 2018, 33(7):119-132.
|
| [3] |
李辉. 论西方文化消费理论研究的范式与主题[J]. 山东师范大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2018, 63(3):53-70.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
傅才武. 文化和旅游融合研究:内在逻辑与政策路径[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2021.
|
| [6] |
宋瑞, 杨晓琰, 谢朝武, 等. 新阶段文旅消费潜力释放与持续健康发展的建议和对策[J]. 河北大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2024, 49(2):22-36.
|
| [7] |
于秋阳. 在线文旅新空间的消费特征与建构机制[J]. 旅游学刊, 2021, 36(7):10-12.
|
| [8] |
郭英之. 研判青年文旅消费的新需求[J]. 人民论坛, 2023(18):25-29.
|
| [9] |
何云梦, 徐菲菲, 剌利青, 等. 基于S-O-R理论的文旅消费驱动机制研究[J]. 旅游科学, 2023, 37(1):116-132.
|
| [10] |
杨懿, 廉倩文, 丁玲, 等. 国家级夜间文旅消费集聚区空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43(6):202-210.
|
| [11] |
陈波, 涂晓晗. 旅游休闲街区消费场景的模式类型与文旅融合策略[J]. 南京社会科学, 2023(8):134-145,166.
|
| [12] |
邹驾云. “沉浸式”体验助力文旅消费提质升级[J]. 人民论坛, 2020(15):84-85.
|
| [13] |
刘震, 杨勇. 互联网使用与家庭文旅消费——兼论互联网普及下居民消费升级的可行性[J]. 旅游学刊, 2022, 37(2):75-93.
|
| [14] |
王亚南. 全国各地城乡居民文化消费比较[J]. 云南社会科学, 2008(5):88-92.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
郭熙保, 储晓腾, 王艺. 文化消费指标体系的设计与比较——基于时间利用的新视角[J]. 消费经济, 2015, 31(6):44-50.
|
| [17] |
王亚楠. 中国文化消费区域差异影响因素研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017.
|
| [18] |
朱媛媛, 甘依霖, 李星明, 等. 中国文化消费水平的地域分异及影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40(3):110-118.
|
| [19] |
贾旭东. 高品质生活视域下的文化消费——基于居民消费支出的考察[J]. 山东社会科学, 2022(2):76-83,92.
|
| [20] |
余凤龙, 黄震方. 中国农村居民旅游消费研究进展[J]. 经济地理, 2017, 37(1):205-224.
|
| [21] |
魏翔, 潘禹, 王明康, 等. 主观意愿能撬动旅游消费吗?——以家庭旅游中的“预先保证”行为为例[J]. 经济管理, 2020, 42(12):168-183.
|
| [22] |
汪德根, 王旭, 陆林, 等. 申遗历程和政策引领视角下中国大运河研究演进脉络与特征[J]. 旅游学刊, 2024, 39(11):149-170.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
侯兵, 金阳, 胡美娟. 空间生产视角下大运河文化遗产重生的过程与机制——以扬州运河三湾生态文化公园为例[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(3):160-171.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
金阳, 张蕴涵, 侯兵. 演化视角下大运河遗产旅游利用的路径与机制——以中国大运河江浙段沿线城市为例[J]. 旅游学刊, 2024, 39(8):53-69.
|
| [27] |
时少华. 京杭运河传统村落非遗活态保护传承与旅游深度融合发展模式研究[J]. 北京联合大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2023, 21(6):51-60.
|
| [28] |
张环宙, 应舜, 吴茂英. 文化型旅游目的地游客感知意象的主题识别与非对称性效应——以运河城市绍兴为例[J]. 地理科学, 2022, 42(12):2131-2140.
|
| [29] |
毛中根. 中国文化消费提升研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.
|
| [30] |
刘军. 空间经济学视域下文化旅游消费发展水平测量[J]. 商业经济研究, 2021(3):50-54.
|
| [31] |
赵卫军, 张爱英, Muhammad W A. 中国文化消费影响因素分析和水平预测——基于误差修正与历史趋势外推模型[J]. 经济问题, 2018(7):59-66.
|
| [32] |
余凤龙, 侯兵, 张爱平. 转型时期苏南地区农村家庭旅游消费特征及影响因素研究[J]. 旅游科学, 2019, 33(3):81-95.
|
| [33] |
王文姬, 曹鲁娜. 共同富裕视域下数字普惠金融对文化消费差距的影响研究[J]. 南京社会科学, 2023(1):149-158.
|
| [34] |
朱迪. “宏观结构”的隐身与重塑:一个消费分析框架[J]. 中国社会科学, 2023(3):26-46,204.
|
| [35] |
张苏缘, 顾江. 文化消费试点政策对城市产业结构升级的影响研究[J]. 当代经济科学, 2022, 44(3):111-122.
|
| [36] |
唐承财, 刘亚茹, 万紫微, 等. 传统村落文旅融合发展水平评价及影响路径[J]. 地理学报, 2023, 78(4):980-996.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
谢彦君, 卫银栋, 胡迎春, 等. 文旅融合背景下海南国际旅游消费中心的定位问题[J]. 旅游学刊, 2019, 34(1):12-22.
|
| [39] |
凌欢, 程励. 非对称视角下区域旅游经济差异形成机制研究——基于31个省(区、市)的清晰集定性比较分析[J]. 旅游科学, 2023, 37(4):161-182.
|
| [40] |
陆林, 余凤龙. 中国旅游经济差异的空间特征分析[J]. 经济地理, 2005, 25(3):406-410.
|
| [41] |
何昀, 谢迟, 毛中根. 文化消费质量:内涵刻画、描述性评价与现状测度[J]. 财经理论与实践, 2016, 37(5):115-120.
|
| [42] |
张明, 杜运周. 组织与管理研究中QCA方法的应用:定位、策略和方向[J]. 管理学报, 2019, 16(9):1312-1323.
|
| [43] |
罗文斌, 楚雪莲, 刘阳杰. 复杂视角下乡村旅游地农户可持续生计组态影响研究——以成都市幸福村为例[J]. 旅游学刊, 2024, 39(7):112-126.
|
| [44] |
秦宗财, 从菡芝. 我国文化带文旅融合升级研究——基于大运河文化带江苏段的测度[J]. 山东大学学报 (哲学社会科学版), 2022(6):49-59.
|
| [45] |
厉建梅, 单梦琦, 齐佳. 大运河文化带沿线城市文化—生态—旅游耦合协调发展[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(10):201-207.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |