

RCEP Tourism Service Trade Network: Evolutionary Characteristics, Conjugate Circulation Effects and Formation Mechanism
Received date: 2024-12-30
Revised date: 2025-04-10
Online published: 2025-06-24
Exploring the evolution characteristics and mechanisms of the tourism service trade network is of great significance for promoting regional economic development. Based on the WTO-OECD Balanced Trade in Services Database (BaTIS) in 2001-2021, this paper uses the methods of complex network analysis and TERGM to explore the dynamic evolution features and formation mechanism of the tourism service trade network of RCEP member countries. Results show that: 1) The conjugate space of tourism service trade of RCEP member countries gradually expanded, showing a typical "small world" network characteristic. The tourism service trade network of RCEP member countries shows the obvious phenomenon of central polarization, and its spatial distribution is unbalanced. 2) China, Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand are increasingly playing pivotal roles in conjugated circulation. Developing countries in the lower circulation establish close links with developed countries in the upper circulation through conjugation effect, and evolve into three cohesive sub-groups which take China, Australia and Singapore as the cores. 3) The tourism service trade network has reciprocity effect, grade effect and time dependence effect. Per capita GDP, population density, government efficiency and border connection have significant impact on the formation of the tourism service trade network. According to the above, it puts forward some suggestions to promote the RCEP member states to jointly build a more open, inclusive and mutually beneficial tourism service trade network: giving full play to the core role of emerging economies in the conjugate circulation, strengthening the supply capacity of high-quality tourism service products in the "upper circulation" of tourism service trade, fostering mutually beneficial and coordinated development among developing countries in the "lower circulation", improving the market access mechanisms of various countries in the trade circulation and promoting the digital transformation of the tourism service trade circulation.
WANG Juan , ZHANG Huan , WEI Rongjie . RCEP Tourism Service Trade Network: Evolutionary Characteristics, Conjugate Circulation Effects and Formation Mechanism[J]. Economic geography, 2025 , 45(4) : 210 -220 . DOI: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2025.04.020
表1 TERGM主要变量及含义Tab.1 Main variables and explanation of TERGM |
| 变量名称 | 表达式 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 边(Edges) |  | 网络中边的数量 |
| 互惠性(Mutual) |  | 网络节点形成双向贸易关系的倾向 |
| 三元组(Triple) | 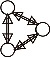 | 网络中3个节点两两相连的结构 |
| 传递性(Transitivity) | 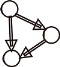 | 网络中3个节点形成如下关系的倾向,i→j,j→k,i→k |
| 循环性(Ctriple) | 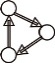 | 网络中3个节点形成如下关系的倾向,i→j,j→k,k→i |
| 变异性(Variability) | 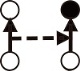 | t期整体网络格局在t+1期发生变异的趋势 |
| 发送者(lnGDPper_se) |  | 节点的发达程度和人口规模对网络中发出关系的影响 |
| 发送者(lnPOP_se) | ||
| 接收者(lnGDPper_re) |  | 节点的发达程度和人口规模对网络中接收关系的影响 |
| 接收者(lnPOP_re) | ||
| 节点属性(PSNV) 节点属性(GovEF) 节点属性(Trade) 节点属性(Continent) |  | 趋同政治稳定程度对旅游服务贸易网络关系形成的影响 趋同国家政府效率对旅游服务贸易网络关系形成的影响 趋同国家贸易规模对旅游服务贸易网络关系形成的影响 趋同国家所属大洲对旅游服务贸易网络关系形成的影响 |
| 接壤关系(Broder) |  | 接壤关系、语言关系对旅游服务贸易网络关系形成的影响 |
| 语言关系(Lauguage) |
表2 RCEP旅游服务贸易网络TERGM实证回归结果Tab.2 Empirical results of TERGM of tourism service trade network of RCEP member countries |
| 网络统计量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 | 模型5 | 模型6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | -10.5562*** | -12.3675*** | -12.1095*** | -12.8253*** | -13.1847*** | |
| Mutual | -1.3219*** | -0.5645** | -0.4772** | -0.4859** | ||
| Ttriple | 0.2790*** | 0.2644*** | 0.2648*** | |||
| Transitiveties | 0.9673*** | 0.9555*** | 0.9587*** | |||
| Ctriple | -0.7528*** | -0.7241*** | -0.7229*** | |||
| Variability | -0.6738*** | -0.3369*** | ||||
| lnPOP_re | 1.6940*** | 1.6676*** | 0.9700*** | 0.9907*** | 0.8526*** | 0.9988*** |
| lnPOP_se | -0.3073** | -0.0003 | 0.2603** | 0.4163*** | -0.9945*** | 0.4102*** |
| lnGDPper_re | 1.0189*** | 0.9813*** | 0.6381*** | 0.5903*** | 1.8239*** | 0.5969*** |
| lnGDPper_se | 0.0799 | 0.2095 | 0.3442** | 0.3608** | 0.9337*** | 0.3680** |
| PSNV | 0.3744*** | 0.4803*** | 0.3896*** | 0.4396*** | -0.9817*** | 0.4378*** |
| GovEF | -0.7845*** | -0.9117*** | -0.7415*** | -0.7405*** | -2.1025*** | -0.7446*** |
| Trade | 1.4513*** | 1.8425*** | 1.5445*** | 1.6793*** | 0.9376*** | 1.6798*** |
| Language | 0.2113 | 0.2262 | 0.1008 | 0.0484 | 0.0605 | 0.0608 |
| Border | 1.0708*** | 1.3069*** | 1.4687*** | 1.6118*** | 1.1710*** | 1.6088*** |
| Continent | 1.9808*** | 2.4551*** | 2.0891*** | 2.2145*** | 1.2656*** | 2.2204*** |
注:***、**、 *分别表示在1%、5%、10%的水平上显著。 |
| [1] |
姚星, 梅鹤轩, 蒲岳. 国际服务贸易网络的结构特征及演化研究——基于全球价值链视角[J]. 国际贸易问题, 2019(4):109-124.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
文艳, 孙根年, 冯庆. 国际旅游服务贸易比较优势动态演进及中国贸易平衡贡献[J]. 资源科学, 2021, 43(8):1675-1686.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
夏杰长, 季雪飞, 孙盼盼. RCEP区域贸易与旅游耦合效应的网络结构特征及演化规律[J]. 社会科学家, 2022(12):71-79.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
徐文海, 曹亮. 国际旅游服务贸易问题研究:文献述评[J]. 国际贸易问题, 2012(8):101-107.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
王桂玉. 中国与太平洋岛国旅游外交:历史基础、现实动力与路径选择[J]. 太平洋学报, 2021, 29(2):83-94.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
田纪鹏. 国内外旅游服务贸易逆差研究前沿与展望[J]. 旅游学刊, 2019, 34(1):136-148.
|
| [17] |
俞路. 语言文化对“一带一路”沿线各国双边贸易的影响——基于扩展引力模型的实证研究[J]. 世界地理研究, 2017, 26(5):21-31.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
牛华, 兰森, 马艳昕. “一带一路”沿线国家服务贸易网络结构动态演化及影响机制[J]. 国际商务(对外经济贸易大学学报), 2020(5):78-93.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
贺胜兵, 姜思琦, 周华蓉. 环境产品贸易网络的结构特征及演进机制——基于共建“一带一路”国家的实证[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2024, 34(2):81-93.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
彭红枫, 常晓君, 王雪童. 区域全面经济伙伴关系协定的经济效应研究——基于改进的TERGM的分析[J]. 国际贸易问题, 2024 (6):106-122.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
李焱, 梁雪涵, 黄庆波. 海运服务贸易网络结构演变与各国角色识别[J]. 经济地理, 2024, 44(11):13-23.
|
| [27] |
陈友余, 宋怡佳. “一带一路”沿线国家数字服务贸易格局及中国地位分析[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43(6):106-117.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
刑其毅, 裴伟伟, 徐瑞秋, 等. 基础有机化学(第三版)上册[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005.
|
| [31] |
朱秋华. 共轭体系的分类及结构特征[J]. 大学化学, 2021, 36(6):49-62.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
洪俊杰, 商辉. 中国开放型经济的“共轭环流论”:理论与证据[J]. 中国社会科学, 2019(1):42-64,205.
|
| [34] |
何晴倩. 强化还是弱化?欧盟“核心—边缘”关系的再审视——基于全球价值链的分析[J]. 欧洲研究, 2021, 39(5):53-83,6.
|
| [35] |
李敬, 陈旎, 万广华, 等. “一带一路”沿线国家货物贸易的竞争互补关系及动态变化——基于网络分析方法[J]. 管理世界, 2017(4):10-19.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
曹吉云, 佟家栋. 影响区域经济一体化的经济地理与社会政治因素[J]. 南开经济研究, 2017(6):20-39.
|
| [40] |
柴子曈, 刘建民. 经济全球化视野下国际贸易与政府治理的挑战——评《服务型政府与国际贸易管理》[J]. 国际贸易, 2021(10):98.
|
| [41] |
陈伟, 赵晞泉, 刘卫东, 等. “一带一路”贸易网络演化与贸易门户国家识别[J]. 地理学报, 2023, 78(10):2465-2483.
|
| [42] |
刘志彪, 吴福象. “一带一路”倡议下全球价值链的双重嵌入[J]. 中国社会科学, 2018(8):17-32.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
栾心晨, 黄永源, 朱晟君, 等. 被低估的边缘:边缘区域创新研究综述[J]. 经济地理, 2024, 44(11):1-12.
|
| [45] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |